Little Blue Heron
Description
The little blue heron (Egretta caerulea) is a small heron belonging to the family Ardeidae.
Distribution & Habitat
The Little Blue Heron occurs from most of the United States
through Central and South
America including the West
Indies (Biaggi 1997), where it
is generally a common resident
on most of the islands (Raffaele
and others 1998). It is a common
resident in Puerto Rico and can
be seen regularly at the Parque
Centrals boardwalk along
the Caño Martin Peña in the
municipality of San Juan (Oberle
2018). It also occurs on satellite
islands such as Vieques (Sorrié
1975) and Culebra (Kapan 2003),
in the latter being common in
fall, winter, and spring, and
uncommon in summer (Gemmill 2015). Habitat includes mostly
calm and shallow freshwater
and saltwater areas (Raffaele and
others 1998) including ponds,
wetlands, canals, mangrove
swamps, estuaries, and lagoons
(Oberle 2018). The atlas
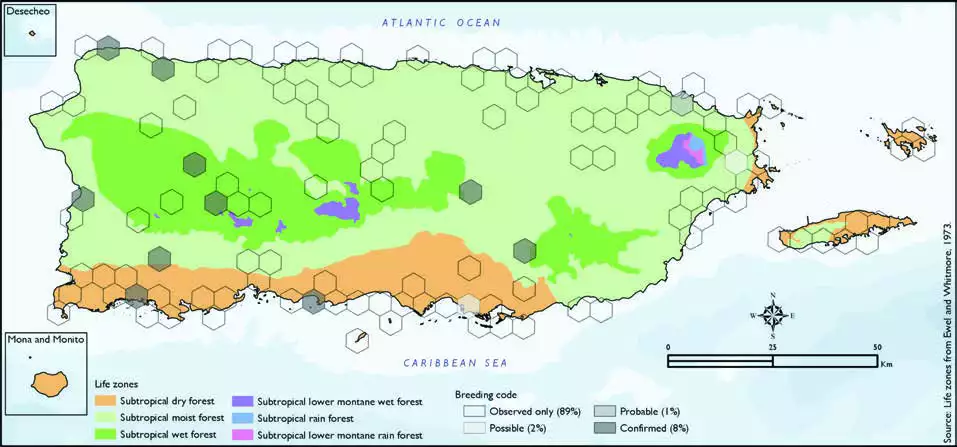
fieldwork yielded a total of 199
records within 118 hexagons
or 25 percent of the 479 total
hexagons (see map). Of the 118
hexagons where this species
was found, breeding met the
atlas definition of confirmed in
8 percent (10) of the hexagons,
probable in 1 percent (1), and
possible in 2 percent (2), while
the species was observed in 89
percent (105) of the hexagons
but without evidence of breeding
(see map).Little Blue Heron distribution. The map shows the highest breeding code by hexagon and overlaying the ecological life zones in
Puerto Rico. Note: percentages may not total 100 due to rounding. 151Little Blue Heron/Garza Azul
Breeding Habits
Previously published reports indicate that the Little Blue
Heron breeds from April to July,
and it is usually colonial with
other heron species (Raffaele and
others 1998). The nest consists of
a platform made mostly of twigs,
which is usually constructed
high in trees (Raffaele and
others 1998) or in bushes near
water (Biaggi 1997). Atlas
results indicate that this species
breeds from March to June and
sometimes in August, with the
most breeding activity during
March and June (see chart).
Overall, the breeding activity mostly takes place within the
subtropical moist forest life zone
(see chart). Results show that
this species breeds mostly within
subtropical moist (62 percent of
the hexagons) and subtropical
dry forest life zones (23 percent
of hexagons) (see table). It also
breeds within subtropical wet
and lower montane wet forest
life zones at higher elevations
(15 percent of the hexagons)
(see table and map).
Conservation
The current overall population trend of the Little Blue Heron
is described as decreasing, although some populations
have unknown trends (Wetlands
International 2012). However,
this species is currently listed
as a species of least concern by
the IUCN (BirdLife International
2017). Locally, this species is not
listed in any of the threatened
categories of PRDNER and
USFWS. In Puerto Rico, the Little
Blue Heron has a protected
habitat in land of 11 percent or
33 km2 of the total area covered by the hexagons where evidence
of breeding was found for this
species (311 km2).
Related Species
Family:
heron